请求调度器 接口 提供调度request到另一个资源(servlet/jsp/html)的功能。
The RequestDispatcher interface provides the facility of dispatching the request to another resource it may be html, servlet or jsp.
该接口也可以用incloude方法包含另一个资源(servlet/jsp/html)的内容。它是servlet协作的一种方式。
This interface can also be used to include the content of another resource also. It is one of the way of servlet collaboration.
在RequestDispatcher接口中定义了两种方法: forward和include
forward
public void forward(ServletRequest request,ServletResponse response)throws ServletException,java.io.IOException:
Forwards a request from a servlet to another resource (servlet, JSP file, or HTML file) on the server.
如下图所示,servlet2的response发送给客户端。2而servlet1的response不会显示给用户。
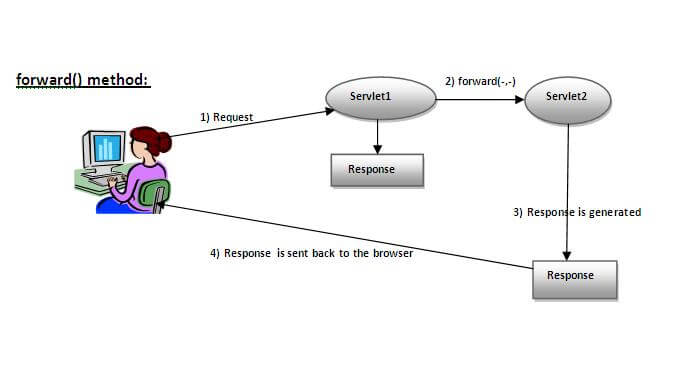
ServletRequest接口的getRequestDispatcher()方法返回RequestDispatcher的对象。句法:
public RequestDispatcher getRequestDispatcher(String resource);
例子
RequestDispatcher requestDispatcher = request.getRequestDispatcher("/sessionLoginDemo/login.jsp");//得到转发器
requestDispatcher.forward(request, response);//转发(调度)请求给/sessionLoginDemo/login.jsp 并由login.jsp发送response给客户端。
include
public void include(ServletRequest request,ServletResponse response)throws ServletException,java.io.IOException:
Includes the content of a resource (servlet, JSP page, or HTML file) in the response.
如下图所示,servlet2的response包含在(正在发送给客户端的)servlet1的response包中。
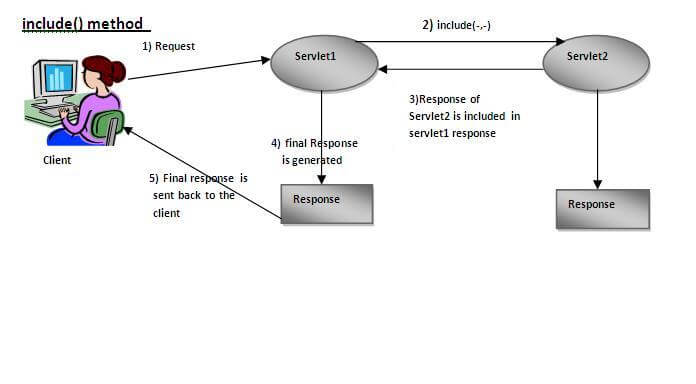
例子
Example of RequestDispatcher interface
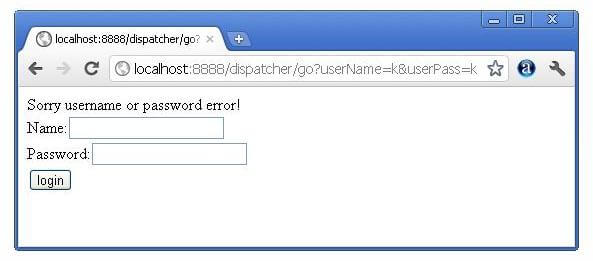
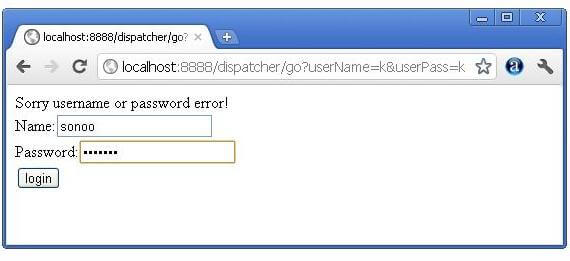
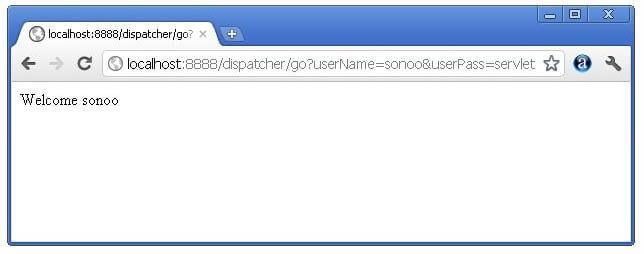
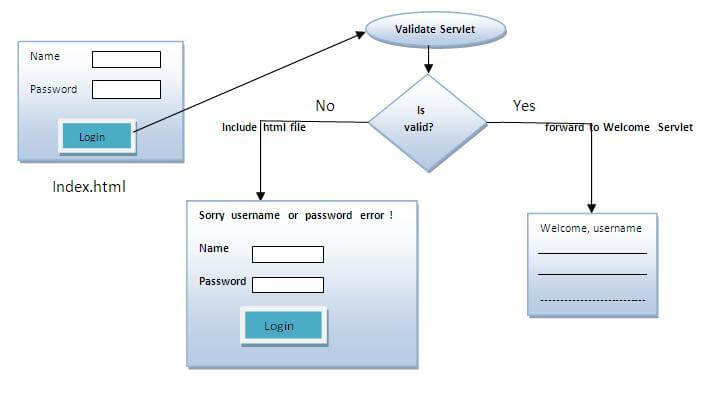
In this example, we are validating the password entered by the user. If password is servlet, it will forward the request to the WelcomeServlet, otherwise will show an error message: sorry username or password error!. In this program, we are cheking for hardcoded information. But you can check it to the database also that we will see in the development chapter. In this example, we have created following files:
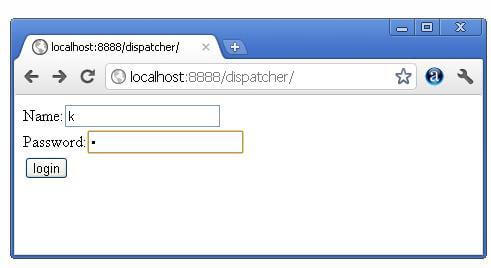
index.html file: for getting input from the user.
Login.java file: a servlet class for processing the response. If password is servet, it will forward the request to the welcome servlet.
WelcomeServlet.java file: a servlet class for displaying the welcome message.
web.xml file: a deployment descriptor file that contains the information about the servlet.
index.html
<form action="servlet1" method="post">
Name:<input type="text" name="userName"/>
Password:<input type="password" name="userPass"/>
<input type="submit" value="login"/>
</form>
Login.java
import java.io.*;
import javax.servlet.*;
import javax.servlet.http.*;
public class Login extends HttpServlet {
public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
response.setContentType("text/html");
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
String n=request.getParameter("userName");
String p=request.getParameter("userPass");
if(p.equals("servlet"){
RequestDispatcher rd=request.getRequestDispatcher("servlet2");
rd.forward(request, response);
}
else{
out.print("Sorry UserName or Password Error!");
RequestDispatcher rd=request.getRequestDispatcher("/index.html");
rd.include(request, response);
}
}
}
WelcomeServlet.java
import java.io.*;
import javax.servlet.*;
import javax.servlet.http.*;
public class WelcomeServlet extends HttpServlet {
public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
response.setContentType("text/html");
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
String n=request.getParameter("userName");
out.print("Welcome "+n);
}
}
web.xml
<web-app>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>Login</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>Login</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>WelcomeServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>WelcomeServlet</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>Login</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/servlet1</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>WelcomeServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/servlet2</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<welcome-file-list>
<welcome-file>index.html</welcome-file>
</welcome-file-list>
</web-app>
download this example (developed in Myeclipse IDE)
download this example (developed in eclipse IDE)
download this example (developed in netbeans IDE)