模拟醉汉随机漫步
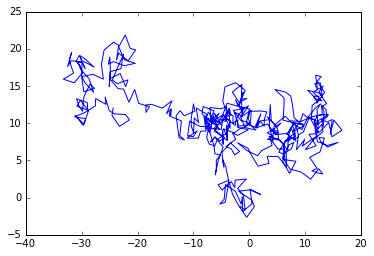
假设醉汉每一步的距离是1或2,方向也完全随机,360度不确定,然后模拟醉汉的行走路径.
我们用坐标表示醉汉的位置,每次产生两个随机数,一个是步长,就是醉汉一步走多远,我们假设1或2,r = np.random.randint(1,3,N),一个是方向,是一个度数,0-360,theta = np.radians(np.random.randint(0,361,N)),注意转化为弧度,每走一步,坐标值就是之前坐标值之和,用cumsum函数可以很方便地实现,x = np.cumsum(r*np.cos(theta)),y = np.cumsum(r*np.sin(theta))。然后ok了,plot一下看看醉汉的步伐有多醉人。
N = 500 # steps
r = np.random.randint(1,3,N) # move 1 or 2 units of distance each step
theta = np.radians(np.random.randint(0,361,N))
# np.cumsum Return the cumulative sum of the elements along a given axis.
x = np.cumsum(r*np.cos(theta))
y = np.cumsum(r*np.sin(theta))
plt.plot(x,y);
img